MOTA
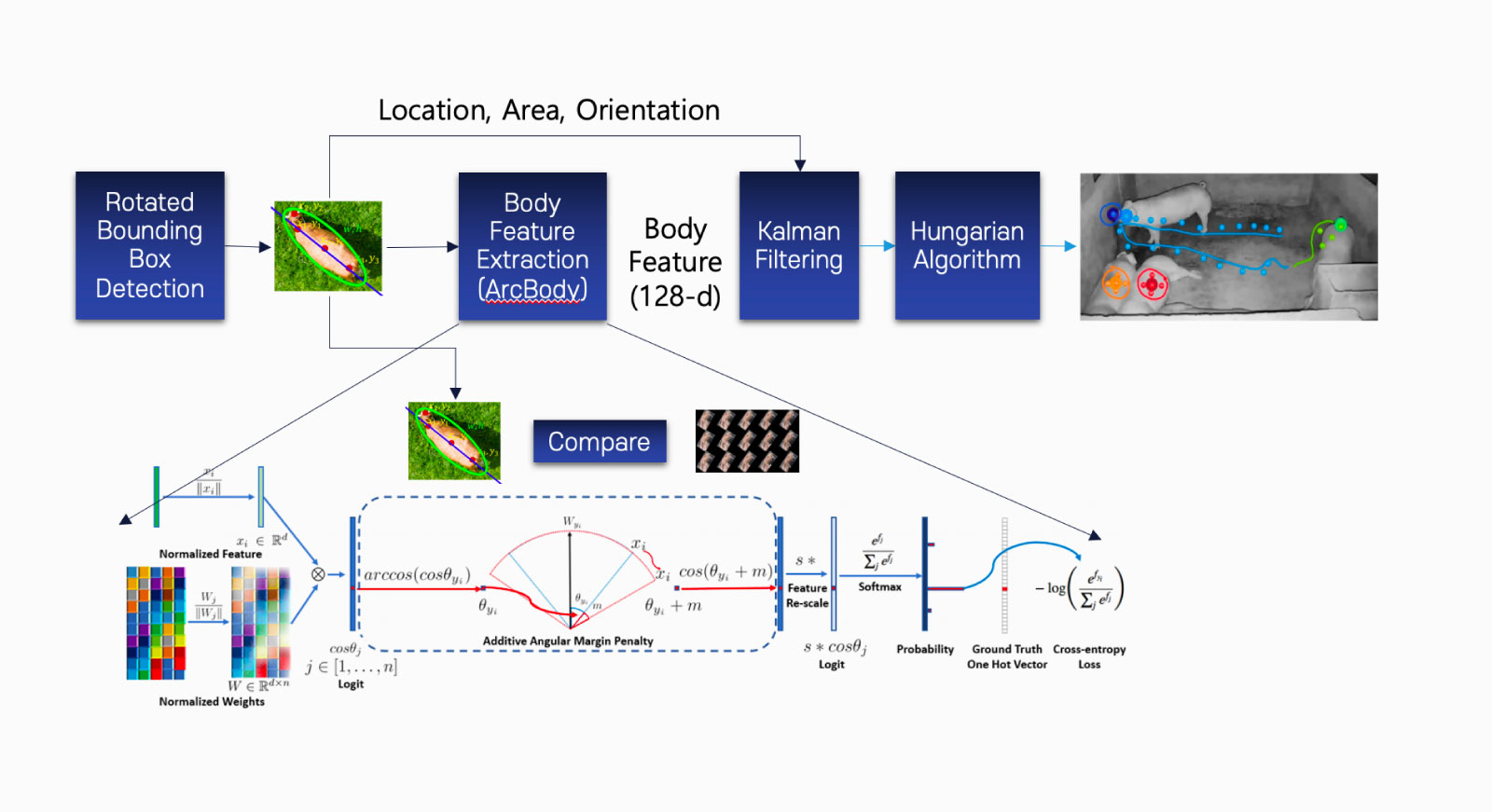
Even genetically identical piglets can be tracked without sensors or barcodes, using only the camera.
mAP50
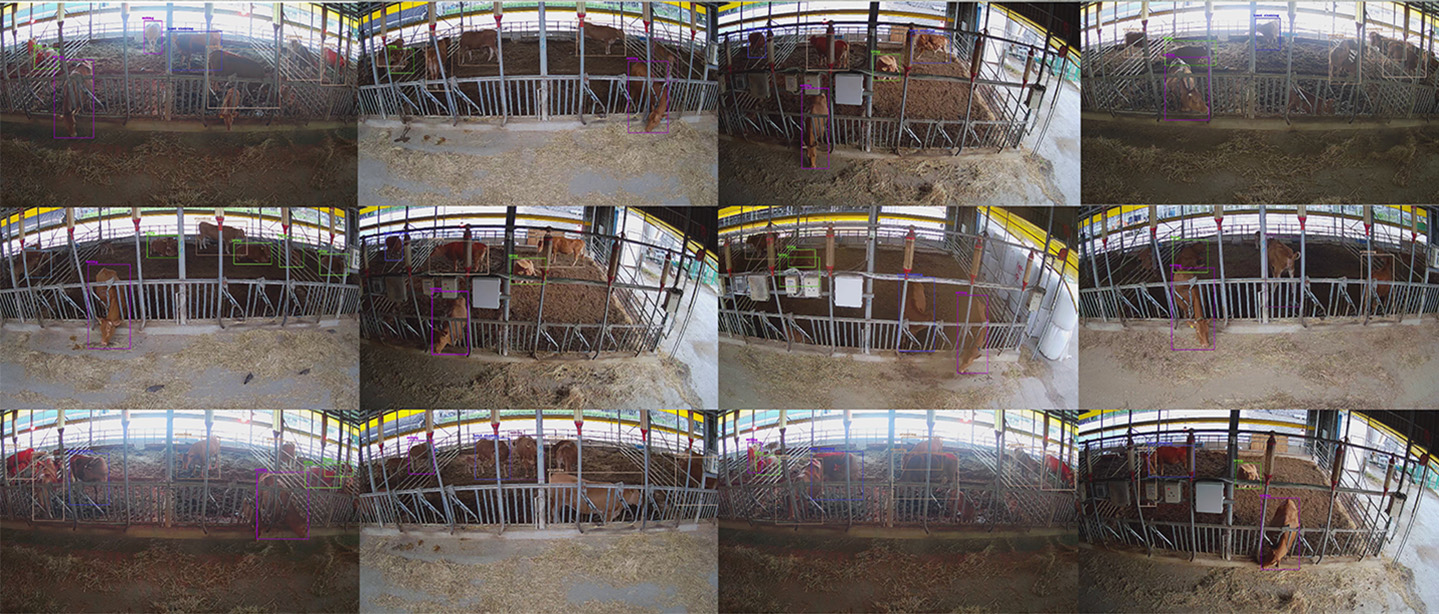
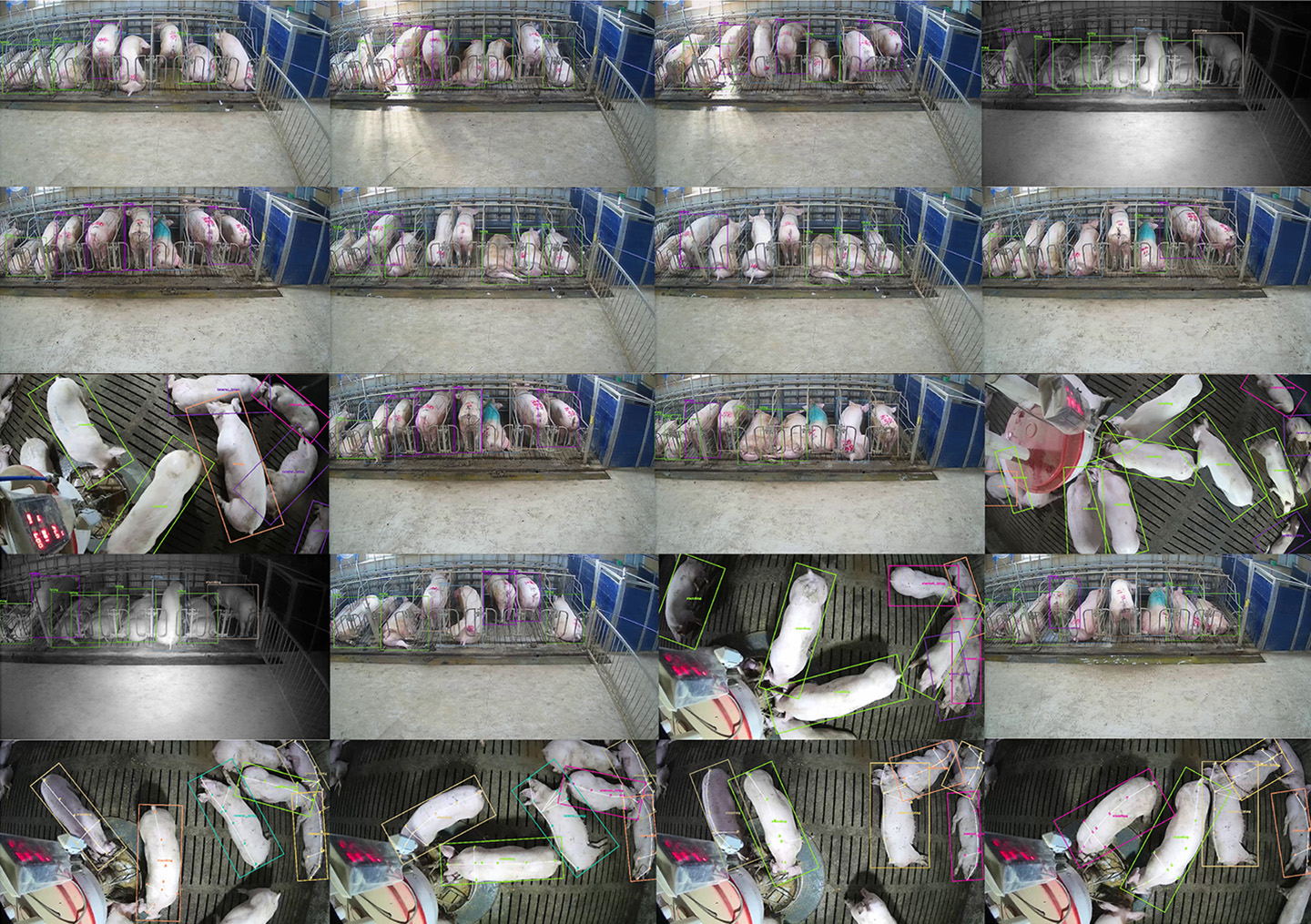
Real-time classification of various postures of livestock such as pigs, cattle, and dairy cows. Analyzes 4 postures for pigs and 7 postures for cattle, applicable in areas such as feed management, disease monitoring, and estrus detection.
Individual Posture Data
The posture classification AI model, trained on over 2,500,000 individual posture data points, classifies everything from basic postures to unique animal-specific postures in real-time.
Cattle Individual Posture Data

Pig Individual Posture Data

| NO | Behavior Classification | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Standing | Standing cattle that do not engage in other behaviors (e.g., tail raising, eating, head scratching). |
| 2 | Lying Down | Cattle with their chest touching the ground. |
| 3 | Eating | Cattle extending their head outside the fence while eating. |
| 4 | Head Scratching | Cattle performing head scratching or with their head bent. |
| 5 | Tail Raising | Standing posture with the tail raised. |
| 6 | Sitting | Cattle with their hindquarters and back legs touching the ground, while only the front legs are extended. |
| 7 | Mounting | Posture of standing on another cow with the front legs, while the rear legs remain on the ground (applies only to the cow on top). |
| NO | Behavior Classification | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Standing | The pig is standing with all four legs on the ground, head up, and facing forward. |
| 2 | Lying Down | The pig is lying down with its chest touching the ground, or lying on one side with its belly facing upwards and one side of its back touching the ground. |
| 3 | Eating | The pig is in a standing posture with its head lowered towards the feed trough. |
| 4 | Sitting | The pig is lying down with its hindquarters and back legs touching the ground, while only its front legs are extended.우 |
video
Individual Movement Tracking
and Posture Classification
Movement and posture data of multiple animals over time
(time, individual ID, location, posture)
Data Preprocessing
(feature extraction, normalization, and standardization)
Unsupervised Learning (k-means, DBSCAN)
for data analysis
Extraction of group behaviors occurring at specific times
(aggregation, dispersion, mounting, fighting, feeding)